CloudStack Webhooks Framework | CloudStack Feature First Look

Event notifications enable real-time communication of critical events to external systems and users. They allow key actions and changes to be promptly reported, supporting immediate response and integration with other services. For example, event notifications can alert administrators for resource utilization thresholds, or system failures, enabling proactive management and automation. Likewise, users can receive alerts […]
ShapeBlue Takes the Stage: Expert Sessions at CloudStack Collaboration Conference 2024

The ShapeBlue team is excited to be participating once again at the CloudStack Collaboration Conference! Taking place in the vibrant city of Madrid, Spain, from November 20-22, the event is set to be another #CSCollab to remember. The first day will kick off with a hackathon, followed by two days filled with sessions and workshops, […]
CloudStack Storage Browser | CloudStack Feature First Look

Over time, the Primary and Secondary Storages exhaust their available space, requiring CloudStack Administrators to actively manage and free up these resources. Although administrators can view the stored files, they cannot determine whether these files are associated with any CloudStack Volume, Snapshot, Template, or ISO Image. To solve this, Apache CloudStack 4.19 introduced a new […]
Event Roundup: CloudStack European User Group 2024

We were pleased to see that this year’s CloudStack European User Group was another productive and useful event for the CloudStack community. It was great to have ShapeBlue CEO Giles Sirett and Technical Marketing Manager Marco Sinhoreli hosting their own sessions. We were also happy to sponsor the event alongside LINBIT and proIO, who served […]
NFS Mount Options on Primary Storage | CloudStack Feature First Look

Previously, when mounting Primary Storage on a KVM hypervisor host, CloudStack used default NFS mount options that could not be customized. Administrators were unable to modify or add options such as specifying the NFS version or adjusting the nconnect value, which defines the number of TCP connections between the hypervisor and the NFS server. This […]
US Signal Shifting Workloads to Apache CloudStack After Losing Predictability with VMware

Following the challenges arising from Broadcom’s acquisition of VMware, US Signal sought an additional IaaS solution to offer their customers. John White, Chief Operating Officer at US Signal, emphasizes the importance of companies controlling their own destinies and having full opportunities for cloud consumption. US Signal is a leading digital infrastructure provider offering cloud, […]
ShapeBlue Team Members will be presenting at the CloudStack European User Group 2024

The ShapeBlue team is excited about the upcoming CloudStack European User Group 2024, scheduled for September 19th in Frankfurt. Hosted by proIO, a leading German Private Cloud and Managed Hosting Provider, this event will feature a day of insightful CloudStack-focus presentations. We are excited to see ShapeBlue CEO, Giles Sirett and Technical Marketing Manager, Marco […]
Hosting a Static Website using CloudStack and MinIO

This tutorial describes how to configure CloudStack together with Minio Object Storage bucket to host a static website. MinIO is an Apache licensed open-source distributed object server, designed to be compatible with Amazon S3, which makes it easy to have the same API interface Static websites do not need server-side programming and databases. They contain […]
Choosing the Right Hypervisor: Apache CloudStack Hypervisor Support
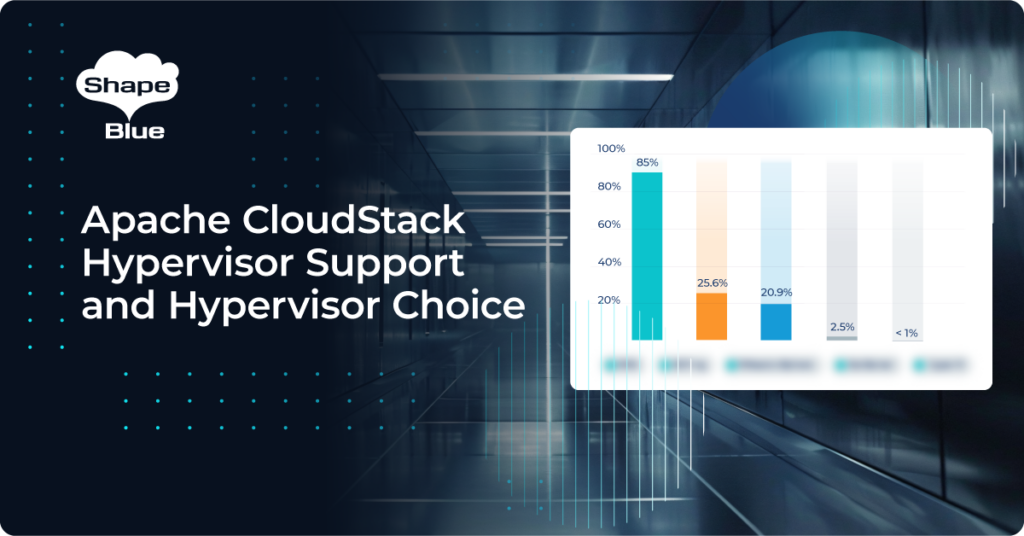
Apache CloudStack stands out by supporting multiple hypervisors, offering organisations the flexibility to choose the one that best meets their specific business needs. This article analyses the three key hypervisors supported by CloudStack: KVM, VMware vSphere and XCP-ng / XenServer. We will examine their features, architecture, performance metrics, and suitability for various workloads and explore […]
KVM Import | CloudStack Feature Deep Dive

Among hypervisors chosen by organisations, KVM stands out as a popular open-source option. While standalone KVM setups and those coupled with virtualization management tools serve many purposes effectively, there’s a growing interest in self-service, multi-tenant IaaS cloud orchestration solutions like Apache CloudStack. This trend is driven by the enhanced features, scalability, and the overall cloud […]