What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing architecture that brings computing capabilities to the network’s periphery, closer to the data’s source, where it can be processed locally without the need to ship it back to a centralized computing resource. This drastically reduces latency, thus enabling real-time processing while lowering bandwidth costs.
The edge architecture model has seen a massive growth in recent years, and the rise of IoT devices only exacerbates the need for on-site computing capabilities, while the widespread adoption of more modern data transmission technologies (such as 5G networks) reduces costs and facilitates the deployment of edge computing. There is an expectation for exponential year-on-year growth in the number of Edge devices deployed.
Challenges and Benefits of Edge Computing
The primary tenet of Edge Computing is to keep storage and processing as close as possible to the data origin, eliminating the long round trip to a remote data center. Edge computing is a wise choice for the industrial and manufacturing sectors, considering the large amount of data generated by IoT devices such as sensors, cameras and robots. Keeping data close to the source is a wise and lower-cost option, which in addition to delivering a higher quality of service when compared to redundant interconnections to remote data centers or IaaS Platforms also helps to avoid issues related to compliance, security and high latency.
See what the Gartner’s Group “Market Guide for Edge Computing” says;
“It must be easy to use and manage, connect seamlessly and enable compute capabilities from simple filtering to rich machine learning where needed in the distributed computing value stream. Edge computing can be delivered as a service, or through hardware and software deployed in the path of data flow — at or near the edge.”
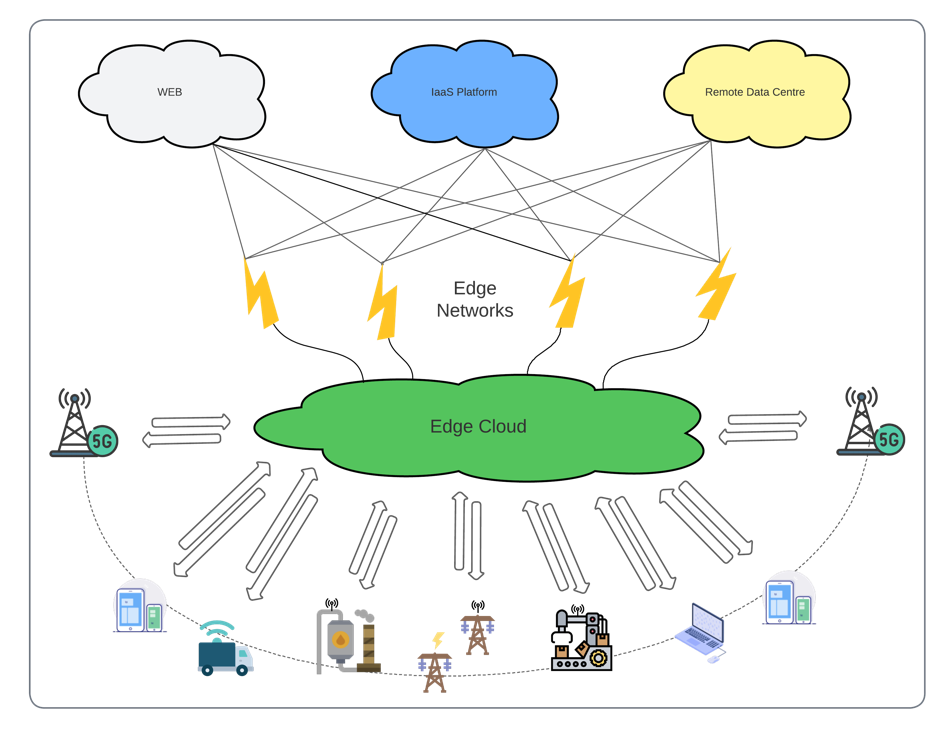
In summary, enterprises and service providers require an easy and centralized pane of glass to orchestrate distributed edge zones, managing and deploying compute, storage, and network resources, as they currently do in a traditional CloudStack environment in the data center, bringing control from a single endpoint. In this aspect, CloudStack is the right choice, proven to be a robust, reliable, and secure platform for distributed core and edge zones at scale.
Use Cases
The adoption of edge computing brings many advantages to diverse business verticals by solving issues related to high bandwidth consumption and high latency in response time.
Apache CloudStack, a proven, production-ready IaaS cloud platform, supports the broadest edge computing use cases: centralizing management of both traditional Cloud (Core Zones) and Edge Zones from a single pane of glass.
Hospital monitoring
Currently, devices such as glucose monitors, heart rate monitors and other sensors are not connected or, when they are, they are connected to external computing resources, being subject to high latency and low throughput of data transmission for processing. This is a latent concern for health professionals, since in many cases they have a short response time in which to react to changes in patient’s conditions.
Regarding edge computing within hospitals, it enables monitoring and analysis systems to be close to the medical devices, allowing real-time notification on changes, in addition to providing important data on trends in the health status of patients through AI analysis and also allowing for the creation of dashboards with a complete real-time view of a patient’s status.
Predictive maintenance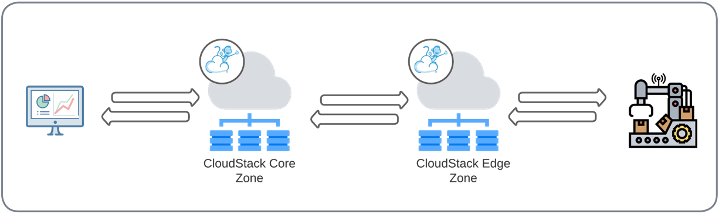
With the goal of analysing and detecting unwanted changes in production lines as a consequence of equipment failures, manufacturers can use CloudStack Edge Zones to bring processing closer to the data storage, thus allowing IoT sensors to monitor the integrity of their machines with very low latency and be able to extract data for real-time analysis and remediation.
Autonomous IoT vehicles
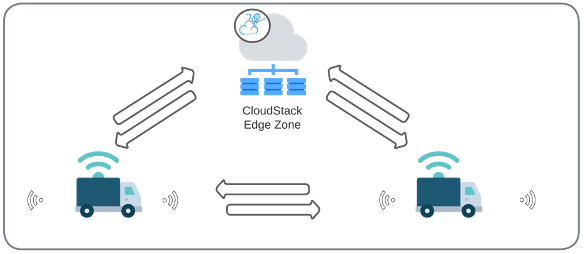
All autonomous vehicles on the road utilize edge computing AI programs, which are often trained using data centre based machine learning capabilities. In this use case, IoT devices can collect data on road conditions, average speed, acceleration patterns, etc. This data can then be processed locally by a CloudStack Edge Zone node and be used to save fuel and reduce congestions. In this specific case, the need for drivers in the convoy can also be eliminated, except for the front one.
Remote monitoring
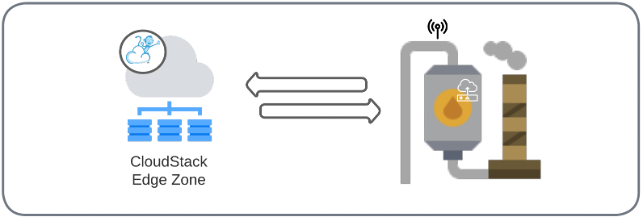
Failures in factory devices, oil or gas processing sites or power plants can be disastrous and lead to environmental impact. In order to avoid this scenario, all assets must be carefully monitored. Deviations should be detected and resolved as quickly as possible. This can be very challenging and costly given their geographically isolated nature.
The use of CloudStack Edge Zones allows for real-time data analysis, enabling automated intervention and predictive maintenance of critical infrastructure.
Content delivery
With the growing number of end-user devices connected and consuming content such as music, video, web pages and other resources at the end of the network, content caching systems reduce the utilization core network links while improving content delivery. In this scenario, latency is reduced considerably, since the content being accessed is cached close to its end-users.
Content providers benefit from this model by expanding their CDNs further to the edges of the network, thus ensuring flexibility and reducing duplicated traffic in the core network, whilst improving the experience of end-users, especially in remote locations.
Smart grid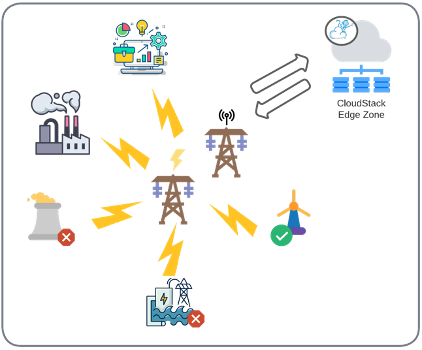
IoT devices and sensors in factories, offices, homes and power plants can be used to monitor energy usage and production in real-time. Suppliers can then leverage CloudStack Edge Zone capabilities deployed at key points in the grid to analyze the usage data and adapt energy production and delivery according to the immediate demand, leading to higher production and transmission efficiencies and allowing for seamless integration of green energy sources into the grid.
Traffic management
Traffic management can also benefit from Edge Computing. Traffic optimization such as bus frequency based on demand fluctuation, extra lane management and self-driving car flow management are examples of how Edge Computing can be utilized.
Smart homes
Smart homes are highly dependent on IoT devices that collect information from around the home. Currently, this data is typically transmitted to a central cloud where it is processed and stored. This architecture presents problems related to the high cost of backhaul, latency and security.
By using Edge Computing to bring processing and storage closer to IoT devices, there’s no need for the data to be transmitted outside the home, and this sensitive information can be processed locally. For example, voice assistant responses could be much faster, allowing for a more immersive user experience while increasing security.
Apache CloudStack Edge Zones
Edge environments are typically constrained in space, power and bandwidth making the deployment of full-fledged CloudStack Zones, with multiple hypervisor hosts, storage arrays, and switching infrastructure, either cost prohibitive or technically unfeasible.
From Apache CloudStack 4.18, operators can leverage the functionality of deploying lightweight Zones in edge locations. This is achieved by reducing the complexity of the Zone construct, with resources like shared storage, external switching and System VMs not being required for Edge Zones.
This new feature will be a part of the Apache CloudStack 4.18 release.
Marco Sinhoreli works as a Technical Marketing Manager at ShapeBlue. Marco has a depth of experience in helping big organisations implement CloudStack. He has been consulting major companies in Brazil for their CloudStack environments. In addition, he has a strong understanding of the struggle that cloud builders and IaaS providers can experience and how open-source technologies and ACS can help them. Away from work, Marco is a lover of music (playing a mean guitar) and politics.